What Is SOX Compliance?
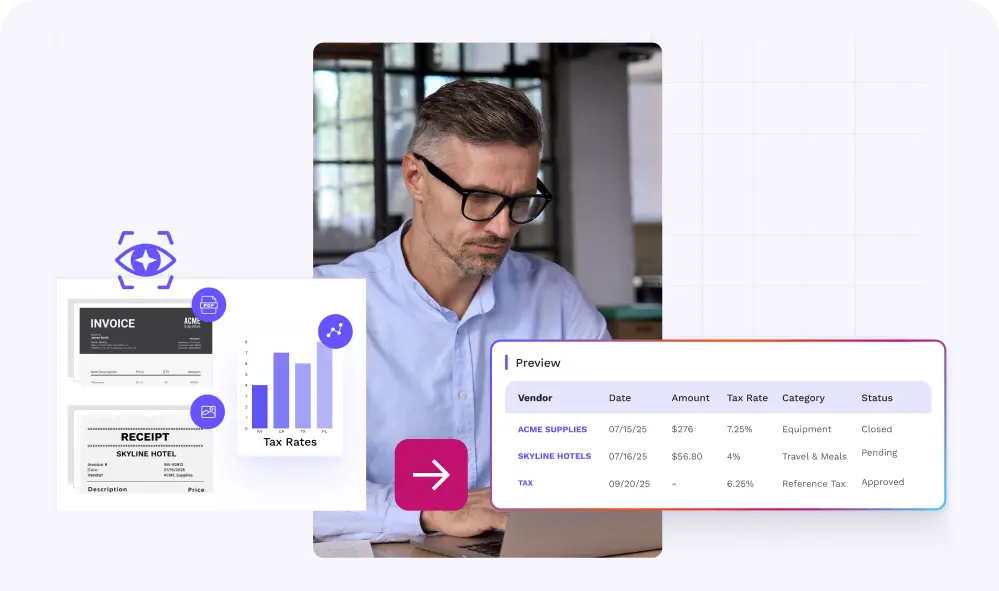
SOX Compliance refers to adhering to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, a U.S. law enacted in 2002 to protect investors from fraudulent financial reporting by corporations. It requires strict controls over financial data integrity, security, and disclosure. This act was created in response to several major corporate accounting scandals, such as Enron and WorldCom, that resulted in significant financial losses for investors.
Importance of SOX Compliance
SOX Compliance is crucial for businesses to ensure transparency and accountability in their financial reporting. It helps protect investors’ interests and maintains the integrity of financial markets. Non-compliance with SOX can lead to severe consequences for companies, including legal penalties, fines, reputational damage, and loss of investor trust.